Assignment Code and Solutions Submission
In the course, you will be submitting your code and/or solutions for the
assignments using git, through Github Classroom.
Brief Overview
Assignments are distributed through github classroom an assignment-specific is posted on Canvas assignment. Accepting the github classroom assignment creates a specific repository for you. Typically, issues for assigmnent steps are created at the same time.
To work on your assignment:
- Clone your repository.
- Make your modifications and make commits.
- Push the commits to the remote repository as you go
When the deadline for the assignment is reached, the latest (most recent) commit to the repository will be taken as the final solution and this is what will be graded. You do not have to worry about multiple submissions; they are acceptable, however only the last commit is taken into account when the deadline is reached.
Browse your repository on github.com to validate that your latest version is there (and you did not forget to push).
The next sections walk you through the process in more detail in case you are unfamiliar with git / github.
Quick GIT introduction.
Git is a distributed version control system. The purpose of this tool is to track changes in source files through time, following the development of any software or other project.
For more invo you can watch the introduction videos: What is Version Control? What is Git? Get going with Git. For github-specific introduction check out its Get Started page.
Basic git operations
You only need to master a fraction of all of git’s functions in order to successfully submit your work. These operations are outlined next.
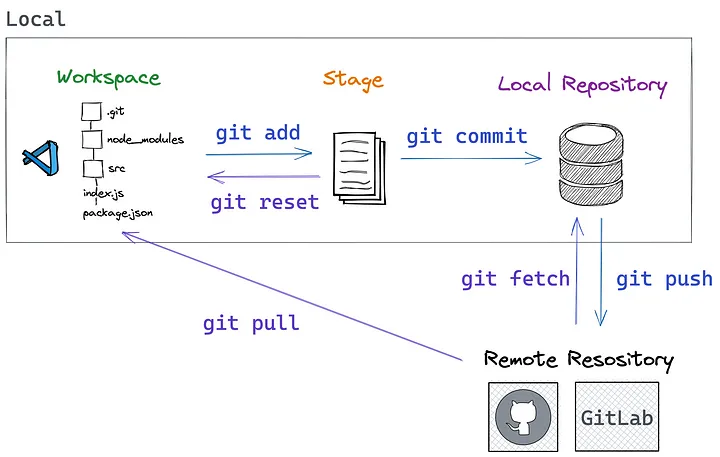
Setting up Github Access
In order to authenitcate using github on a machine (your own, or COE VLAB) you will need to use SSH keys. The following steps setup SSH keys:
- On your target system (e.g. COE VLAB in a terminal, or in your WSL terminal) generate a new SSH key. No need to add the to ssh-agent as they are stored on your target system.
- Then, add the generated key to GitHub
- Test the SSH connnection and authentication
Working on a GitHub Hosted Assignment
In a terminal and folder of your choice (e.g. ~/classes/eece7368):
-
Clone the assignment reop, make to use SSH authentication, for example:
git clone git@github.com:neu-ece-7368-f23/hw1-schirner.gitWould create a directory
hw1-schirnerwith the source tree for working on. -
Work on your local files:
cd hw1-schirner # edit files and solve the assignment - A typical flow making changes, includes
- show local changes
- add (stage) changed files to be committed
- commit staged files into the local repo
- With every commit provide a small message (ideally < 80 characters), expressing what the changes in this commit entail. Include the issue number (e.g. #2) in your commit message.
- As git is a distributed version control system,
commitsthat you issue locally in your machine are indeed local. Nobody else sees them yet.
- push to github
- In order to have those
changes submitted to the remote server (github in our case), you must do
a
git pushoperation. This will send all the local commits you have made that are not in the remote repository yet. - Validate your changes made it to github by visiting your repo’s website.
- In order to have those
changes submitted to the remote server (github in our case), you must do
a
- Git workflow illustrates the process graphically.
Please do not add output files (e.g. object files, executables) or temporary files that are produced in the compilation process into the repository. Since these files can be easily recreated (e.g. through compilation) they would just clog the repository without much use.
Git interactions are also integrated into many editors, e.g. GIT in VSCode
Submodules
Git submodules are a great way to integrate working across multiple sources. This may come in handy for larger repositories such as in the project phase.
Read about submodules: